The extensive information on the internet about optimizing for search engines can be overwhelming, especially for those new to the field. This article aims to systematize this knowledge, providing a clear understanding of basic SEO concepts. You’ll find a straightforward approach to learning SEO with step-by-step instructions and curated resources. It makes it easier for beginners to grasp the fundamentals and apply practical techniques to improve SEO in Google.
Please feel free to watch the video related to the guide instead of reading:
How Do Search Engines Work?
Google and other search engines help us find needed information, make purchases, and order services. But how does the search engine work?
The processes inside search platforms like Google consist of three components:
- page scanning;
- page indexing;
- page ranking.
Let’s see how they operate:
1.Scanning. At this stage, Google crawlers go through pages of the site to find new content or changes in existing content. Scanning occurs before pages are added to the search engine index.
2.Indexing. This is the process of adding pages to the search engine database. Some pages should not be added to the database, so they are closed from indexing.
3.Ranking. This is the most important part for an SEO specialist. It is a distribution of places in the search result. Neither Google nor its competitors fully disclose the algorithms for ranking, so most of our knowledge is collated through experiments, continuous data collection, and analysis.
Ranking can be challenging. SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) are diverse and constantly changing in different locations. There are three key factors to consider concerning this matter:
- Relevance. Google and its competitors are constantly working to give the most complete and accurate answer to user search queries.
- Geolocation. Millions of users are looking for products and services in their vicinity. Such requests are called geo-dependent searches. The usual search results may differ for geo-dependent searches, as they are affected by the searcher’s location. SEO specialists should take this into account when promoting websites.
- Personalization. Google often shows the sites you have visited before and considers the peculiarities of your behavior. It is called personalization.
SEO Terminology
SEO has professional terminology that beginners should familiarize themselves with. Let’s review a few fundamental conceptions:
URL — the site’s address, page, image, or file. It includes three main parts:
1.HTTP or HTTPS protocol;
2.the domain name of the site, for example, website.com;
3.page address, for example, “/services”;
4.parameters.
Snippet — a block of information about the page that is displayed in search results. An informative snippet is crucial as it helps to drive more traffic to the page.
Landing page — a website page that primarily converts traffic into targeted visitor actions. These visitor actions could be applications, purchases, event registration, etc.
We have a detailed guide on how to optimize CTA (call-to-action) for landing pages.
Search query — a keyword that the user enters in the search bar to obtain specific information.
Intent — the user’s intention and need when entering a specific search term. Intent can be a purchase of goods, search for technical information, etc. Understanding the types of intent to display your site pages for relevant search queries is essential.
Backlinks — hyperlinks to web pages from other sites. Usually, the anchor text of these links is a search query.
Search volume — the total count of searches conducted for a specific keyword in the search bar over a designated timeframe.
Keywords are typically categorized based on their search frequency into three groups: high-volume (exceeding 1K searches per month), mid-volume (up to 1K searches per month), and low-volume (fewer than 100 searches per month). This metric is crucial for understanding keywords’ popularity and potential impact within SEO strategies.
Crawling is checking website pages by a search engine robot (crawler) to detect new and updated content before adding it to the search index.
The search index is a database of pages and sites collected and stored by the search engine. Sites are ranked based on this information.
Meta tags are HTML elements that provide additional structured information about the content on the page.
Read more in the guide for meta tags by Google.
What is Search Engine Optimization?
SEO promotion (Search Engine Optimization — optimization for search engines) is a series of website enhancing tasks to improve its ranking in the SERPs and get additional traffic.
What is the main focus of SEO – Key Metrics
In business and marketing, evaluating the effectiveness of all actions is imperative. This also applies to the SEO. Here are three main metrics that SEO specialists are guided by:
1.Traffic. The most prominent SEO task is attracting maximum visits from the search engine result page. Such traffic is called organic traffic. The constant growth in the number of visitors from Google is one of the signs that SEO is effective.

In this blog article, you will learn what other KPIs to consider. If all three indicators grow, SEO is effective.
What does website SEO include?
SEO encompasses an enormous scope of work for target sites and other competing sites. Let’s review this process and break it down into its main components.
Two main components include:
We will list a few more here that you should consider.
On-Page Optimization
This is the first stage of search engine optimization. It includes:
- Keyword research. Preparing a keyword **** (a list of queries to attract organic traffic). Serpstat keyword analysis reports will help you cover the topic thoroughly and drive more traffic.
- Site structure. It can be built with a ready-made keyword list. This structure should reflect the central topic of the site, simplify the search for the desired content, and help attract traffic.
- Meta tags. They help search robots to correctly rank content and influence the clickability of content in the search results (CTR).
- Headings. This is the first thing the user sees on the page. It is essential that the H1 heading contains the keyword and reflects the content of the page. For example: “Smartphones of X brand” or “Legal advice in Kyiv.”
- Content on the page. To promote the site, you need correctly optimized and commercial texts. This will bring more traffic to the site and increase conversions.
- Alt attributes. This image attribute allows you to add a textual description of an image or photo so that crawlers understand the content.
Once you have all the components sorted out, you can proceed with the next phase of SEO optimization.
Technical Optimization
This stage includes the code and interface, which should ensure its fast and stable operation and a good user experience. Before starting this stage, conducting a technical audit is necessary. The report will show all the errors and shortcomings identified and grouped by priority.
Here are the components of technical SEO optimization:
- Setting up URLs. All links on the site should be formed using common logic according to the site structure. Also, URLs should be human-readable (friendly URLs), avoiding using number sets and special characters. An article on the Serpstat blog will help you configure friendly URL addresses for site pages.
- Finding and fixing 404 errors. Broken links on a site can be a big problem. This is often why users need help finding what they are looking for and may leave forever. It is essential to identify and eliminate any errors before proceeding with further tasks.
- Setting up the robots.txt file. This is a system file that contains instructions for search engines. It suggests which pages to index and which not. Google has created a detailed guide for creating and configuring robots.txt.
- Creating a sitemap. A sitemap is a file listing all the website’s URLs for search robots to discover and crawl. Read more about sitemaps in the Google guide.
- Site speed. Amazon has calculated that a page load slowdown of just one second could cost up to $1.6 billion in sales in a year. This is an essential indicator of site performance. To check the loading speed of a website, you can use the following method: Google Pagespeed Insights or Serpstat Audit.
- Secure connection. Having a secure https protocol on your site is an important ranking factor. It ensures the site’s and user data’s protection and increases the site’s credibility.
- Duplicate pages and headers. Content on all pages must be unique. URLs with partially repeated content should be closed from indexing.
- Redirects (301/302). You often redirect traffic from one page to another when working on a site. Problems with setting up redirects can seriously reduce the effectiveness of SEO.
Read more about redirects here.
Technical optimization is often done simultaneously with on-page optimization to save time. You can proceed to the next stage when all the work is done.
Off-Page Optimization
Off-page optimization increases the number of natural links on the site and mentions of the company on other resources. This is done by the SEO specialist or by a separate member of the team — a link builder.
Local SEO
Local SEO works for website promotion by considering the business’s location and the customers’ geography. Main differences of local SEO:
- The site is promoted, firstly, on requests related to a specific area. It can be a city, several cities, or even a region.
- Links for the site are drawn mainly from local resources.
- One main targeted action will be a client’s visit to the office, workshop, or company’s offline store.
We recommend the Serpstat study on the most popular “near me” queries, as it will help you determine where local SEO will be relevant.
Content Strategy
For successful SEO, a content strategy is necessary. Work with content continues once photos of products, descriptions of categories, and texts on service pages are published on the site. Content strategy is a detailed plan for creating posts and distributing all types of content. It includes texts, videos, images, etc. By using Serpstat AI reports, you can analyze the content.
Let’s add the analytics setup to the SEO content activities list. Analytics allow you to evaluate work effectiveness and, if necessary, adjust the SEO strategy.
Why is SEO Important?
In most cases, SEO becomes the most essential marketing tool. Why? The main reason is that it works at all stages of the purchase funnel:
- Awareness stage. Visitors at this stage come to the site for information queries. They arrive at the site using such queries as: “The best smartphones of 2024” and “What tool does an electrician need?”. These visitors mostly read blog posts.
- Interest stage. Users at this stage also come via information queries, but the set of these keywords is different. Most often, these are keywords like “Which phone is better?”, “How to do a keyword research?”. Such visitors often view articles with reviews rather than category pages.
- Decision. Traffic at this stage arrives through commercial queries: “buy a laptop” or “order SEO services.” Visitors look at the pages for services, categories, and product cards.
- Action. The site’s contact forms and checkout pages are crucial at this stage. They must work flawlessly.
SEO also improves visitor retention. If the promoted site is in the top results for a particular product, the likelihood that a visitor will return is much higher.
Who is SEO Suitable For?
SEO works for brand awareness, audience expansion, and traffic and is suitable for almost all types of businesses. Within SEO, you can use various strategies that allow you to tailor the results to the needs of a particular company.
Common SEO Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions and unrealistic expectations associated with SEO. You should know about them:
- “It would be best if you focused on high-volume queries.” This is a mistake. The competition for high-volume queries is huge. It is much easier and faster to reach the top by ranking for hundreds of low-volume search keywords.
- “SEO and contextual advertising on Google can’t be blended.” This is not true. These tools work well together. However, choosing the correct queries for displaying ads and allocating resources is crucial.
- “The customer does not need to monitor the results of the work of an SEO specialist.” Many entrepreneurs believe paying for services and waiting for a huge traffic flow is enough. This is not true. The best option would be to outline key marketing indicators from the beginning of an arrangement, which the customer and contractor will monitor.
- “As traffic grows, sales will grow.” This is not necessarily true. The SEO specialist also works to convert more visitors into buyers by assessing and improving the technical condition of the site and many other factors.
- “In 2-3 months, you can reach the top for all crucial keywords”. You should not expect ranking any site to be this and make such promises to the client. It all depends on the level of competition in the targeted industry and updates of Google algorithms.
Search Engine Algorithms and Ranking Factors: SEO 101
The most challenging thing to understand is the ranking algorithms and the factors that affect them. Let’s see why this is important.
Search engine algorithms are the patterns to crawl and index the web. They can be represented as a mathematical equation with several unknowns. Each of the unknowns is a ranking factor.
Google ranking algorithms may change their criteria from time to time. This means that something deemed vital yesterday may be less significant tomorrow and vice versa. These continuous algorithm changes are why the SERPS may change drastically over time.
Search engines apply several types of penalties when specific rules are violated:
- A search ban excludes all site pages from the search results and index.
- Pessimization is a decrease in the site rank or the removal of individual pages from the search results.
To do SEO correctly, it is worth focusing on three components:
1.Internal factors. Start to optimize all the site’s technical indicators, conduct a usability audit, and fix errors. Be sure to collect relevant keywords and add high-quality SEO texts while paying attention to keyword density. It should not be too high. Otherwise, the site risks being penalized by search engines for keyword stuffing.
2.External factors. Create high-quality, informative content for your site to get more backlinks and mentions. Analyze competitors to find out what sites they get links from and what link-building techniques they use.
3.Behavioral factors and brand traffic. Work on brand awareness and reputation. The more users know and trust the company, the more time they spend on the site.
Now, let’s talk about the search engine algorithms used and what this means to SEO optimizers.
There are two types of penalties — automatic and manual. People carry out the imposition of penalties in manual mode — assessors — who check the search results and independently view sites at the top. A filter to view such actions can be seen in your Google Search Console:
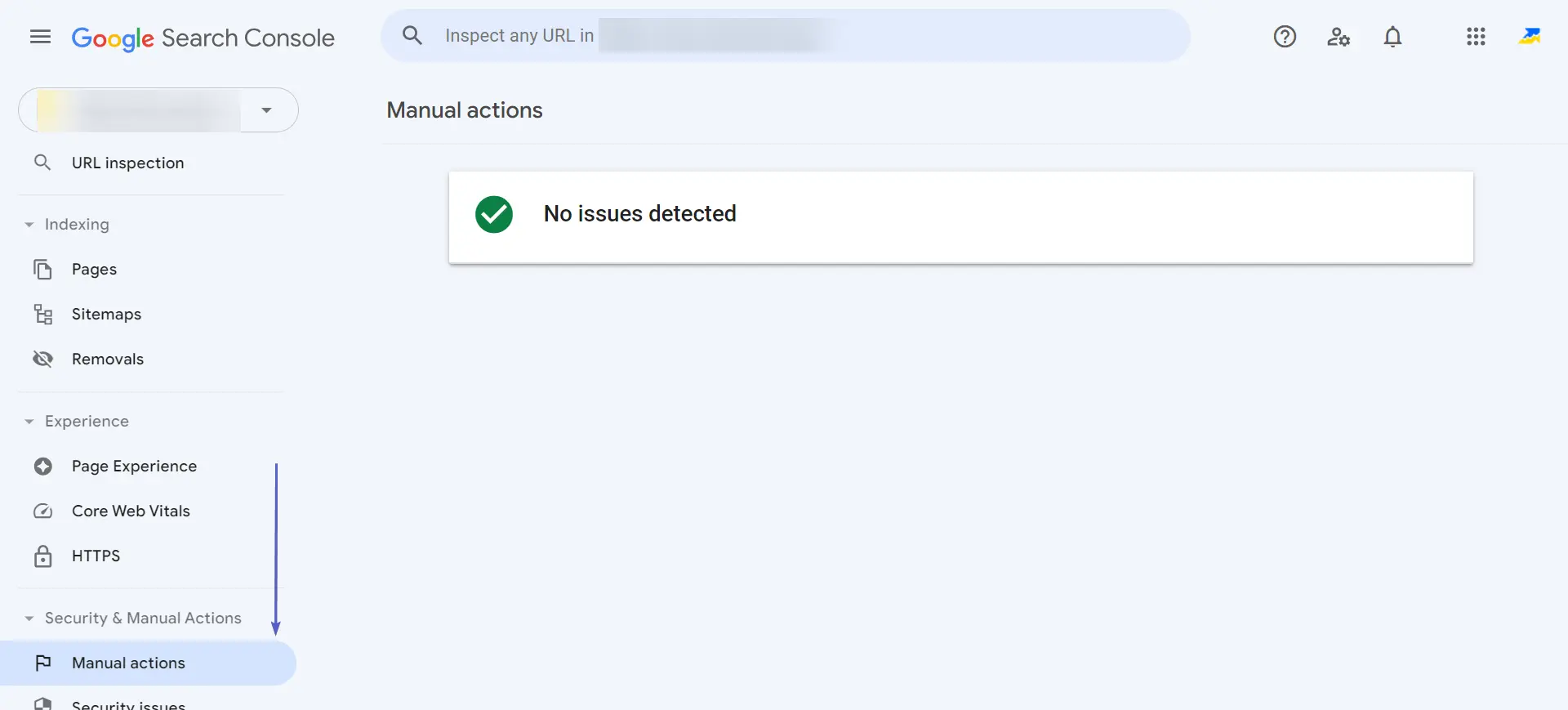
Filters are automatically applied when Google’s algorithms determine that a site violates the Webmaster Quality Guidelines.
Panda Algorithm

Google Panda is Google’s algorithm for evaluating content quality and downgrading low-quality pages. The algorithm has been operating since 2011 and has been modified several times.
The main reasons why websites fall under this search filter are:
- plagiarism of content from other sites;
- keyword spamming in the text;
- pages without much text (up to 400 words);
- low-quality landing pages.
A sharp drop in traffic or numerous pages falling out of the index indicates that a filter may have been triggered.
Penguin Algorithm

Penguin is Google’s algorithm for preventing link spam. It downgrades sites with a lot of purchased links. The algorithm has been in operation since 2014.
Penguin imposes a search filter for several reasons:
- the site has a lot of links with spam anchors;
- there are links from low-quality spam sites;
- there are links from link exchanges and sites for selling links;
- numerous links from non-thematic resources.
A sign that this filter may have affected a site is a sharp rank decrease of 10-20 points. If measures are taken quickly, the decline will continue.
Hummingbird Algorithm
Hummingbird is a Google algorithm designed to show users more relevant search results. For example, if a user enters the query “Where can I find delicious Chinese food in LA”, Google will provide links to the websites of restaurants and cafés.
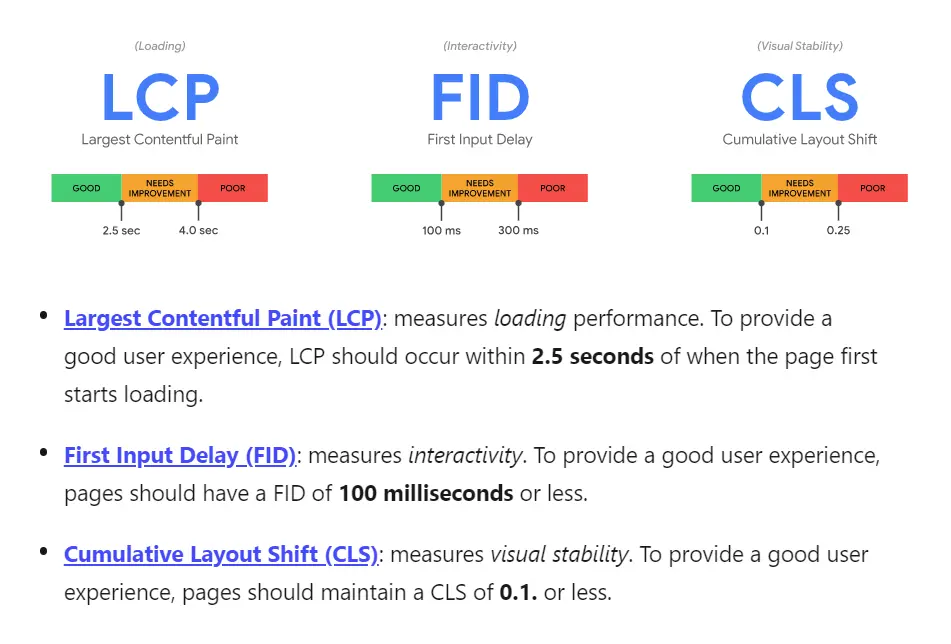
Core Web Vitals

Core Web Vitals is an algorithm aimed at improving the user experience. It displays faster, more user-friendly, and more stable sites above sites that are less optimized. The algorithm considers the site layout’s loading speed, interactivity, and stability.
This blog post provides detailed information on Google algorithms and how to avoid being affected by filters.
Ranking Factors
Ranking factors are criteria used by search engines to evaluate web pages to determine in which order they should be ranked in search results.
In total, Google has more than 200 factors. Most of them are kept secret, and their criteria are regularly adjusted during algorithm updates. SEO experts can confidently determine what helps sites get more traffic through constant experiments and data analysis.
Key ranking factors include:
- content quality
- proper optimization for search queries;
- the number of backlinks and the dynamics of their growth;
- variety of anchor text lists;
- average user spent time;
- bounce rate;
- user-friendly site structure, etc.
We introduced you to SEO and the elements of a search engine. Ranking algorithms may change, but the general logic remains the same. The sites that perform well are the sites that give visitors more helpful information, allowing them to get the right products or services more efficiently.
Conclusion
This guide covered the critical elements to start your SEO journey on the right foot. Embark on this learning path with us and transform how you perceive search engine optimization, turning complexity into clarity.
Pass the test below to make sure you have assimilated all this knowledge 😉
So, You Think You Are an SEO guru? [SEO Knowledge Quiz]
Test Yourself